
CMYK stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow and Key (Black). It’s a color system used in printing.
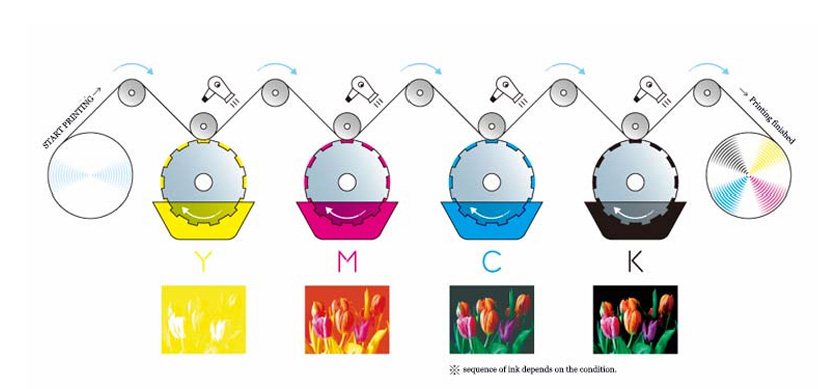
CMYK Printing
Color Mixing: In CMYK, colors are created by mixing varying percentages of the four inks. When used together, they can produce a wide range of colors.
Advantages of CMYK: rich colors, relatively low cost, high efficiency, less difficult to print, widely used.
Disadvantages of CMYK: difficulty in controlling color. A change in any of the colors of the block will result in a change to the end color of the block.
Applications: CMYK is primarily used in the printing process, especially in full-color images or photographs. Most commercial printers use this because it can produce a vast array of colors suitable for different print materials and color designs, image illustrations, gradient colors and other multi-color files.
Color Limitations: While CMYK can produce many colors, it doesn’t include the entire spectrum visible to the human eye. Certain vibrant colors, especially in the greens or blues, may be difficult to achieve.

Spot Colors and Solid Color Printing
Pantone colors or spot colors are a special kind of ink. Spot color printing is used to print large areas of a base color. Spot color printing is a single color with no gradient. The pattern is a field of color and the dots are not visible with a magnifying glass. The inks are pre-mixed for a specific color instead of mixing them in the print.
The most commonly used spot color system is PMS (Pantone Matching System), which gives a standardized color reference. Each color has a unique code, making it easy to achieve consistent results across different prints and materials.
Advantages: spot colors can be more vibrant than CMYK mixes. Spot colors ensure uniformity across different print jobs as the same ink is used. Spot colors can include metallics or fluorescent inks, which cannot be achieved with CMYK.
Applications: Spot colors are often preferred for branding, logos, and when specific color accuracy is crucial, such as corporate materials.

